Unlocking Growth: Use Cases for Business Intelligence Software That Scale
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to gain a competitive edge. One of the most powerful tools available is Business Intelligence (BI) software. This software transforms raw data into actionable insights. It empowers organizations to make informed decisions, optimize operations, and drive growth. This article delves into the diverse use cases for Business Intelligence software that scale. We will explore how these applications help businesses of all sizes thrive.
The ability to scale is crucial. Organizations need solutions that can adapt to their evolving needs. As a company grows, so does its data volume. BI software must handle this increased load without compromising performance or accuracy. This article examines how different industries leverage scalable BI solutions. We will uncover the strategic advantages these tools provide.
Understanding the Core of Business Intelligence
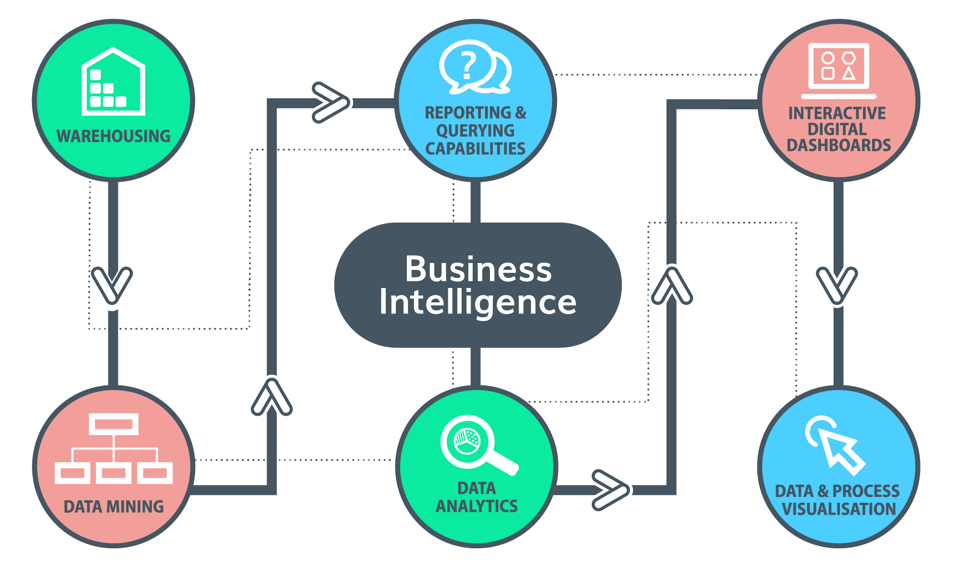
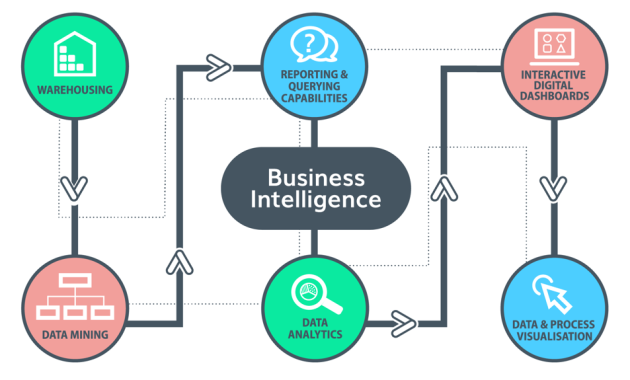
Before exploring specific use cases, it’s essential to understand what constitutes BI. At its core, BI involves collecting, processing, and analyzing data. This process transforms raw data into meaningful information. This information is then used to support decision-making.
Key components of BI include:
- Data Collection: Gathering data from various sources. These sources include databases, spreadsheets, and cloud applications.
- Data Warehousing: Storing data in a centralized repository. This repository is designed for efficient analysis.
- Data Analysis: Applying analytical techniques. These techniques include data mining, statistical analysis, and predictive modeling.
- Data Visualization: Presenting data in a clear and understandable format. This format includes dashboards, reports, and charts.
Effective BI software provides a holistic view of an organization’s performance. This holistic view enables better decision-making. The ability to scale these capabilities is what separates successful BI implementations from those that struggle. Scalable BI systems can grow with the organization.
Use Cases for Business Intelligence Software in Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing departments are heavy users of BI. They use it to understand customer behavior, optimize campaigns, and increase revenue. Here are some specific use cases:
Customer Segmentation and Targeting
BI software analyzes customer data. It identifies distinct customer segments. This segmentation allows marketers to tailor their messaging. It also allows them to target the right customers with the right products. This improves conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
Sales Performance Analysis
BI tools track sales metrics. They provide insights into sales team performance. They identify top performers and areas for improvement. This data helps sales managers optimize their strategies and improve overall sales effectiveness.
Marketing Campaign Optimization
BI software analyzes marketing campaign data. It tracks key metrics. These metrics include click-through rates, conversion rates, and return on investment (ROI). This analysis helps marketers refine their campaigns. This leads to better results and higher ROI.
Lead Generation and Management
BI can be used to analyze lead generation data. It identifies the most effective lead sources. It also helps prioritize leads based on their likelihood to convert. This leads to more efficient sales processes.
Use Cases for Business Intelligence Software in Operations and Supply Chain
Operations and supply chain departments also benefit significantly from BI. They use it to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize processes. Key use cases include:
Inventory Management
BI software analyzes inventory data. It helps organizations optimize inventory levels. It also reduces the risk of stockouts and overstocking. This leads to better resource management and reduced costs.
Supply Chain Optimization
BI tools provide visibility into the supply chain. They track key metrics. These metrics include delivery times, supplier performance, and transportation costs. This allows organizations to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies. They can then optimize their supply chain operations.
Process Optimization
BI software analyzes operational data. It identifies areas for process improvement. This can include streamlining workflows, reducing waste, and improving overall efficiency. This leads to cost savings and improved productivity.
Predictive Maintenance
By analyzing historical data, BI can predict equipment failures. This allows organizations to schedule maintenance proactively. This reduces downtime and prevents costly repairs.
Use Cases for Business Intelligence Software in Finance and Accounting
Finance and accounting departments use BI to improve financial reporting, manage risk, and make better financial decisions. Key use cases include:
Financial Reporting and Analysis
BI software automates financial reporting. It provides real-time insights into financial performance. This includes revenue, expenses, and profitability. This enables finance teams to make informed decisions.
Budgeting and Forecasting
BI tools help create budgets and forecasts. They analyze historical data. They identify trends. They also predict future financial performance. This allows organizations to plan effectively.
Risk Management
BI software helps identify and assess financial risks. It monitors key risk indicators. This enables organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Fraud Detection
BI tools can detect fraudulent activities. They analyze transaction data. They identify suspicious patterns. This helps organizations prevent financial losses.
Use Cases for Business Intelligence Software in Human Resources
Human Resources (HR) departments are increasingly using BI to improve workforce management. They also improve talent acquisition. Key use cases include:
Talent Acquisition
BI software analyzes recruitment data. It identifies the most effective recruitment channels. It tracks the performance of hiring processes. This helps HR teams optimize their recruitment efforts.
Employee Performance Management
BI tools track employee performance metrics. These metrics include sales figures and project completion rates. This provides insights into employee performance. It also helps identify areas for improvement.
Employee Retention
BI software analyzes employee data. It identifies factors that contribute to employee turnover. This allows HR teams to develop strategies to improve employee retention.
Workforce Planning
BI helps forecast future staffing needs. It analyzes workforce demographics. This helps ensure organizations have the right talent in place. This happens at the right time.
Choosing the Right Business Intelligence Software
Selecting the right BI software is crucial for success. Consider the following factors:
- Scalability: Choose a solution that can handle your current and future data volumes.
- Ease of Use: Ensure the software is user-friendly. It should be easy for users to create reports and dashboards.
- Integration: The software should integrate with your existing systems. These systems include databases and cloud applications.
- Features: The software should offer the features you need. These features include data visualization, reporting, and analytics.
- Cost: Consider the total cost of ownership. This includes software licenses, implementation, and maintenance.
The right BI software will depend on your specific needs and budget. Researching different options is important. Evaluate their features and capabilities. Consider your long-term goals. This will ensure a successful BI implementation.
The Future of Business Intelligence
The future of BI is bright. Advancements in technology are driving new possibilities. These include:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming BI. They are automating data analysis. They are also providing more advanced insights.
- Cloud-Based BI: Cloud-based BI solutions are becoming increasingly popular. They offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Self-Service BI: Self-service BI tools are empowering business users. They can analyze data. They can also create their own reports and dashboards.
- Data Democratization: The goal is to make data accessible to everyone. This will lead to better decision-making across the organization.
As technology evolves, BI software will continue to become more powerful. It will also become more accessible. Businesses that embrace these advancements will be well-positioned to succeed. They will leverage data to drive growth. They will also gain a competitive advantage. The various use cases for Business Intelligence software are constantly evolving. This evolution is driven by technological innovation.
Conclusion
Use cases for Business Intelligence software that scale are vast and varied. These applications span across all departments. They empower organizations to make data-driven decisions. They also drive growth and improve efficiency. By understanding these use cases and choosing the right BI software, businesses can unlock their full potential. They can also thrive in today’s competitive landscape. [See also: Best Practices for Data Visualization]